Military Toxics
Differential gene expression and developmental pathologies associated with persistent organic pollutants in sentinel fish in Troutman Lake, Sivuqaq, Alaska
Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) are lipophilic compounds that bioaccumulate in animals and biomagnify within food webs. Many POPs are endocrine disrupting compounds that impact vertebrate development. POPs accumulate in the Arctic via global distillation and thereby impact high trophic level vertebrates as well as people who live a subsistence lifestyle. The Arctic also contains thousands of point…
Read MoreDiffusive fluxes of persistent organic pollutants between Arctic atmosphere, surface waters and sediments
Arctic communities are disproportionately exposed to pollutants from sources including global atmospheric transport and formerly used defense sites (FUDS). The effects of climate change and increasing development in the Arctic have the potential to exacerbate this problem. Yupik People of Sivuqaq, or St Lawrence Island, Alaska are one such community with documented exposures to pollutants from FUDS, and their…
Read MoreElevated mercury and PCB concentrations in Dolly Varden (Salvelinus malma) collected near a formerly used defense site on Sivuqaq, Alaska
Sivuqaq’s proximity to Russia made it a strategic location for U.S. military defense sites during the Cold War. Our results suggest that the Northeast Cape FUD site remains a significant point source of mercury and PCB pollution and contributes to higher concentrations in resident fish, including subsistence species. Moreover, elevated Hg and PCB levels in…
Read MoreLegacy and emerging semi-volatile organic compounds in sentinel fish from an arctic formerly used defense site in Alaska
The purpose of this study was to investigate the extent of contamination from military operations on Alaska’s St. Lawrence Island (Sivuqaq) through the analysis of sentinel fish, the ninespine stickleback (Pungitius pungitius), collected from Troutman Lake located within the watershed of a formerly used defense site and adjacent to the Yupik community of Gambell. The…
Read MoreThreats to Drinking Water and Public Health in Alaska – The Scope of the PFAS Problem, Consequences of Regulatory Inaction, and Recommendations
This investigative report informs actions to address the public health crisis caused by PFAS contamination. In Alaska, the dispersive use of AFFF (aqueous film forming foam) on military bases and airports has contaminated the drinking water of communities from the North Slope to SE Alaska. PFAS have been discovered at over 100 individual sites (mostly…
Read MoreEndocrine disruption and differential gene expression in sentinel fish on St. Lawrence Island, Alaska: Health implications for indigenous residents
We investigated polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) profiles and endocrine disruption in Alaska blackfish and ninespine stickleback living in the vicinity of the Northeast Cape formerly used defense (FUD) site on St. Lawrence Island in the Bering Sea. FUD sites are point sources of PCB pollution; the Arctic contains thousands of FUD sites, many co-located with indigenous…
Read MorePersistent organochlorine pesticide exposure related to a formerly used defense site on St. Lawrence Island, Alaska: data from sentinel fish and human sera
This study examined whether the Northeast Cape FUDS is a source of exposure to organochlorine pesticides. A total of 71 serum samples were collected during site remediation from volunteers that represented three geographic regions of Sivuqaq (St. Lawrence Island). We found elevated levels of pesticides associated with the former military site in the environment and…
Read MoreCommunity-based participatory research projects and policy engagement to protect environmental health on St Lawrence Island, Alaska
This article synthesizes our collaborative community-based research results, interventions and policy engagement for St Lawrence Island, Alaska, during the years 2000-2012.The research team conducted exposure assessment studies that investigated sources from military contamination as well as long range transport.
Read MoreContaminants at Arctic formerly used defense sites
This study found elevated levels of contaminants from the military site at Northeast Cape in sediments and plants, including mercury, mirex and other pesticides, and PCBs. Through congener-specific analysis, we were able to distinguish contaminants from the military sites in the region from those accumulated through long-range transport.
Read MoreFormerly Used Defense Sites in the Norton Sound Region
This report summarizes information about formerly used defense sites in the Norton Sound region, including locations, history, contaminants, and status of clean up. The report also includes a map of the military sites in the region.
Read MorePolychlorinated Biphenyls In Serum Of The Siberian Yupik People From St. Lawrence Island, Alaska
The aim of this study was to determine serum levels of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in Yupik adults from St. Lawrence Island, Alaska, and to determine the relative contribution of atmospheric transport of PCBs and local contamination to body burdens. Our study found that atmospheric transport of PCBs contributes to elevated levels in the Yupik people,…
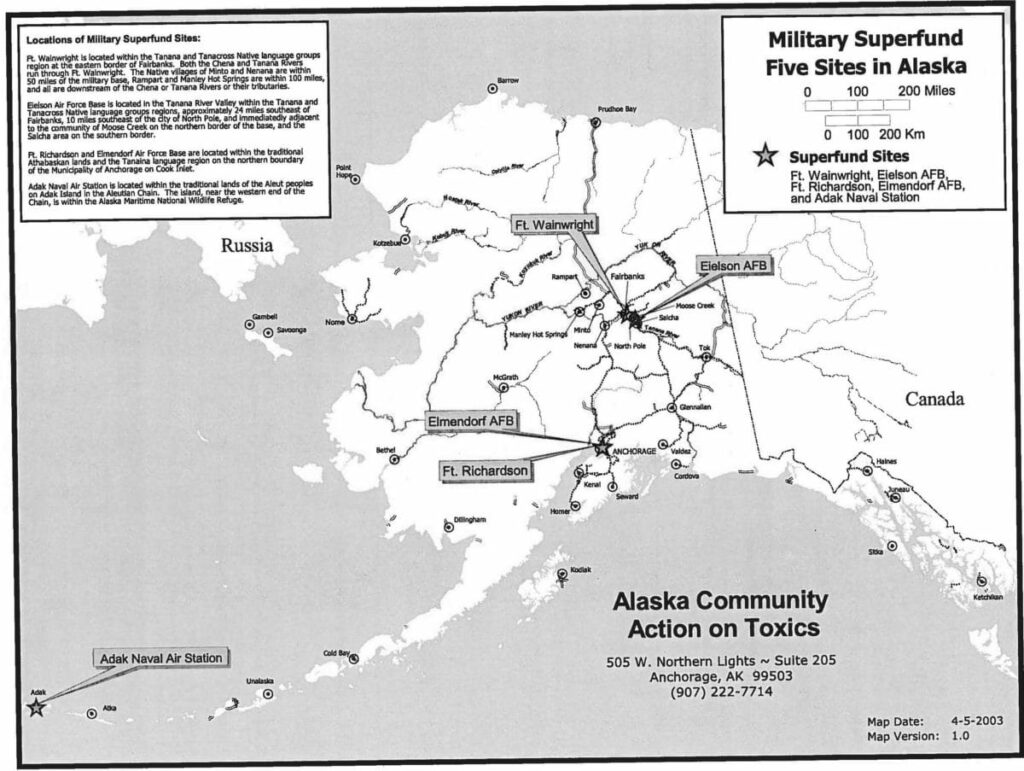
Read MoreEnvironmental Justice and Military Superfund Sites in Alaska
Add report summary here.
Read More